What Is The Difference Between Vitiligo And Albinism?
Since the time you are born, you have pigmentation in your skin that gives it a color. When you are healthy, the skin color will appear normal. However, in specific cases, you will find the color become darker (hyperpigmentation) or go lighter (hypopigmentation). Sometimes, a person may not be born with pigmented skin. Today, you will learn more about vitiligo and albinism, and the difference between the two.
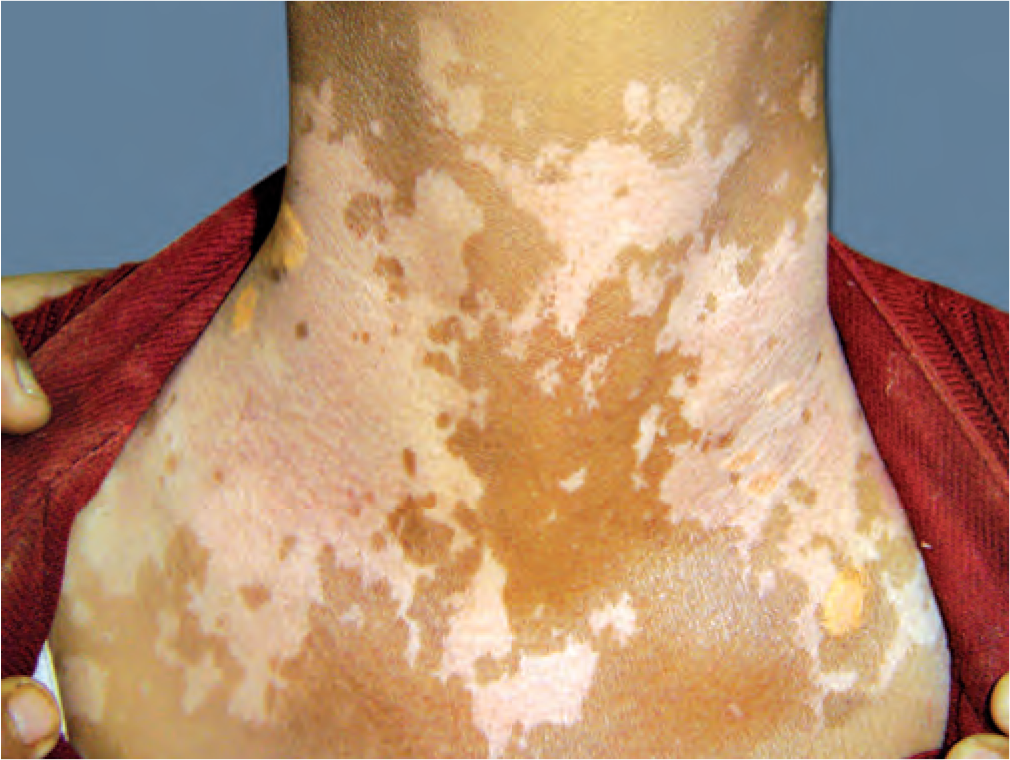
Vitiligo gets characterized by smooth, white patches on the skin. These patches can appear all over the body in some people. It is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the destruction of pigment-producing cells. Although there is no cure for vitiligo, there are several treatments available.
Albinism is a rare inherited disorder caused by a lack of a melanin-producing enzyme. As a result, there is no pigmentation in the skin, hair, or eyes. People with albinism have a defective gene that prevents the body from producing melanin. Albinism cannot get cured.
Now, since you are aware of both vitiligo and albinism, let’s explore the topic further.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Types
Doctors typically categorize vitiligo in the following types:
- When macules appear in multiple locations on the body, it gets referred to as generalized vitiligo.
- Segmental vitiligo refers to a condition limited to one side of the body or one area, such as the hands or face.
- Mucosal vitiligo affects the mucous membranes of the mouth or genitals.
- Focal vitiligo, a rare type in which the macules are concentrated in a small area and do not spread in a predictable pattern within one to two years.
- Trichome vitiligo denotes a white or colorless center, followed by a lighter pigmented area and then an area of normal colored skin.
- Universal vitiligo is a rare type of vitiligo in which more than 80% of the body’s skin lacks pigment.
Albinism results from a mutation in one of the many genes in your body. Depending on that, melanin production can slow down or stop. Now, considering the specific genes affected, albinism can get split into numerous groups and types.
- Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) gets caused by a gene mutation in one of four genes. OCA gets further classified into seven types based on variations.
- An X-chromosome gene mutation causes X-linked ocular albinism. Males are primarily affected by X-linked ocular albinism. Although there are vision issues, the eye, hair, and skin color remain within the normal range.
- Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is a rare variant that is most prevalent in Puerto Rico. The symptoms are similar to those of oculocutaneous albinism, but bowel, heart, kidney, and lung diseases, as well as bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, are more likely.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Causes
Vitiligo Causes
Although the causes of vitiligo are not fully understood, there are several theories:
- Autoimmune disorder: The immune system of the affected person may produce antibodies that destroy melanocytes.
- Genetics: Some factors that may increase the likelihood of developing vitiligo can be inherited. About 30% of vitiligo cases are hereditary.
- Neurogenic factors: A toxic substance to melanocytes may get released at skin nerve endings.
- Self-destruction: Melanocytes destroy themselves due to a defect.
Albinism Causes
A genetic mutation in one of several genes causes albinism. They say that one in every 70 people carries the albinism gene. The genes in question are in charge of several aspects of melanin production, by melanocytes, in the skin and eyes.
The mutations most commonly interfere with the enzyme tyrosinase (tyrosine 3-monooxygenase). This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of melanin from the amino acid tyrosine.
Melanin production can be slowed or completely stopped depending on the mutation. There are always issues with the visual system, no matter how much interference with melanin production. It is because melanin is essential for the retina and the optic nerve pathways development from the eye to the brain.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Risk Factors
Vitiligo Risk Factors
Because the skin has lost its melanin, it no longer has its characteristic color. Melanocytes, the pigment-forming cells, have been destroyed for unknown reasons. We have no idea why this occurs. It could be an autoimmune condition in which your body’s defenses attack your cells rather than invading germs.
Vitiligo may be inherited. You’re more likely to get it if someone else in your family has it or if people in your family have premature grey hair.
Albinism Risk Factors
The most common physical issues associated with albinism are a higher risk of sunburn and skin cancer.
Furthermore, some people are dealing with serious social issues. Bullying at school is one example. Individuals may feel like an outsider due to the constant targeting because of their appearance. Stress, low self-esteem, and isolation can result from these social factors.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Symptoms
Vitiligo Symptoms
Vitiligo symptoms and signs include the following:
- Skin discoloration occurs in patches. It involves your eyes as well as the mucous membranes in your mouth and nose.
- Patches of hair on your head or face turn grey or white before their time.
Albinism Symptoms
Albinism’s primary symptoms include changes in the skin, hair, eye color, and vision.
- A lighter skin tone is the most obvious sign, but skin tone does not always differ significantly. Melanin levels in some people gradually increase over time, darkening skin tone as the personages.
- The individual’s hair color may gradually darken as they age.
- Eyes, too, can change with age, ranging from very light blue to brown. Low melanin levels in the iris cause the eyes to appear slightly translucent and, in certain lighting conditions, red or pink as light reflects off the retina at the back of the eye.
- Albinism always affects vision. It could cause astigmatism, myopia, photophobia, and many other eye-related conditions.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Diagnosis
Vitiligo Diagnosis
During a physical exam, your doctor can usually diagnose vitiligo by looking at your skin. You might also need to take additional tests, such as blood tests and:
- A skin biopsy procedure in which a sample of your skin gets sent to a laboratory for further examination.
- A Wood’s lamp test, in which a doctor examines your skin under UV light.
Albinism Diagnosis
The most common method of diagnosing albinism is through a physical examination. Others include:
- Changes in skin and hair pigmentation get discussed.
- An expert (ophthalmologist) examines the eyes and compares the individual’s coloration to that of the family members.
- Other diseases can also cause pigmentation changes, but they will not cause vision changes.
Albinism is very likely to be the cause if both pigment changes and vision changes are present. Genetic testing is the most reliable way to diagnose albinism. It is not always necessary in families with a history of albinism.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Treatment
Vitiligo Treatment
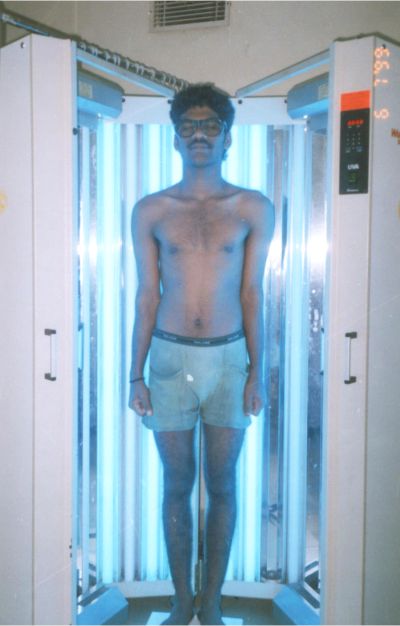
Vitiligo has no known cure. The goal of medical treatment is to achieve a uniform skin tone. Either by restoring color (repigmentation) or removing any remaining of it (depigmentation). The most common treatment options include the following:
- Camouflage therapy
- Repigmentation therapy
- Light therapy
- Surgery
- Counselling
Albinism Treatment
There are no cures for this disease because it is genetic. Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms and monitoring for changes. It is critical to receive proper eye care if you have vision problems. It includes the following:
- spectacles on prescription
- sunglasses with a dark tint to protect the eyes from the sun
- regular eye examinations
You should also watch out for any changes to your skin and use sun protection at all times.
Albinism does not deteriorate with age. A child with albinism can thrive and achieve the same education and employment as someone who does not have the condition.
Vitiligo And Albinism: Who Is Affected?
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disease caused by the immune system attacking melanocytes. As a result, no pigment gets produced, resulting in white spots. Your genetic makeup can predispose you to vitiligo at birth, but the white spots don’t appear on your skin until a chance event occurs. It could happen either internally (which is unknown) or externally, such as a stressful triggering event.
Albinism
Albinism is present from birth as the patient inherits a faulty gene required for melanin production. As a result, melanocytes are present throughout the skin, but because they fail to produce pigment, the skin remains completely white.
When To See A Doctor?
The two conditions get dealt with in different ways. Pigment loss in vitiligo can often get concealed by repigmentation with light therapy. Albinism, on the other hand, gets hard to cover. It is because lack of pigment usually affects the entire body. The only way to deal with it is to protect your skin and eyes from the sun.
By taking the time to understand both these skin conditions extensively, you will raise awareness and help others understand them better. However, if you have further questions, you need to reach out to the right source. To learn more about albinism and vitiligo, speak with your doctor.
At Dr. Paul’s Skin Laser Centre, you will find treatment and consultation for all your skin and hair problems with experts in the industry. With the latest technologies and equipment, you will find yourself in safe hands should you choose to opt for any specific type of therapy. Even when it comes to vitiligo treatment, you will receive efficient solutions that address all your concerns. Therefore, if you choose to opt for vitiligo treatment or learn more about albinism, fill up our online form on the website.
Book An Appointment