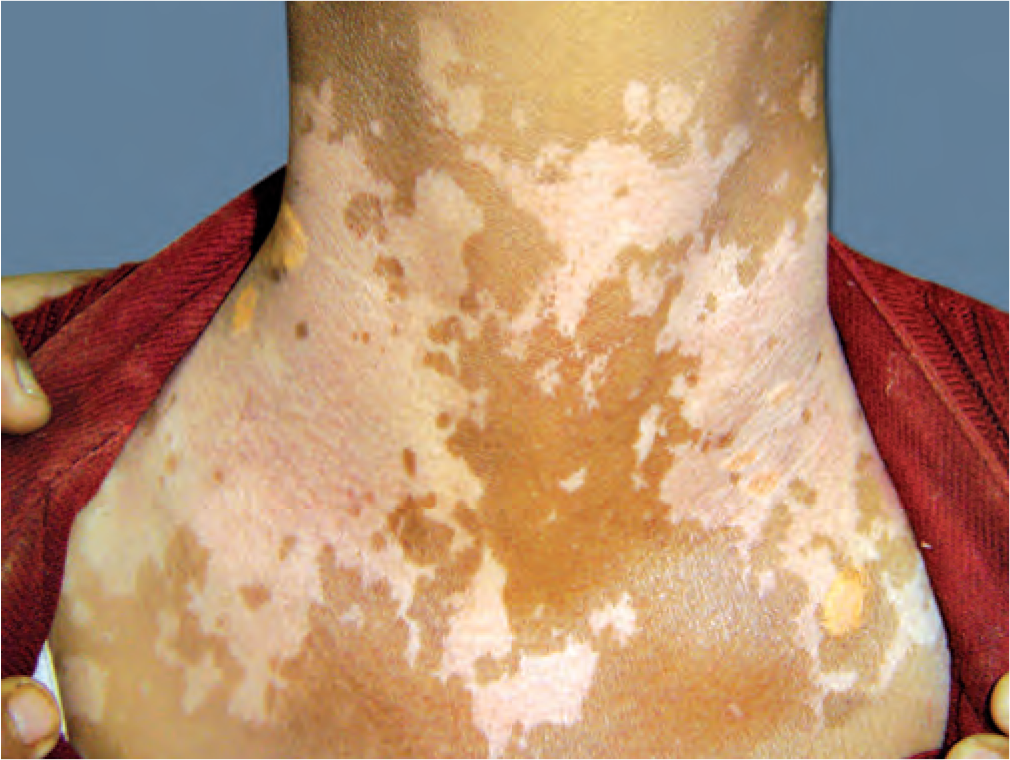
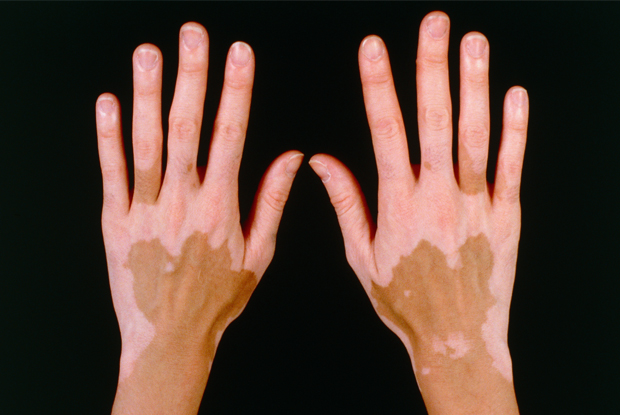
Vitiligo patches (White Patches) are the most difficult variety of vitiligo to manage The primary reason behind failure of treatment in these areas is the absence of viable melanocytes in the skin and the absence of hair follicles ,the second reason behind failure to achieve repigmentation in these areas is that there is disease activity.
The primary reason behind the failure is the absence of viable melanocytes in the skin and the absence of hair follicles as is now evident that the repigmentation in generalized vitiligo following medical therapies is perifollicular (If the hair on the depigmented patches are still pigmented) or it is marginal repigmentation i.e. melanin production from the viable active melanocytes present in the margin of the vitiligo patch.
The second reason behind failure to achieve repigmentation in these areas is that there is disease activity. Even though most of the patches seem to be stablein a case if generalized vitiligo the acral lesions show a very slow but definite spread in many cases and hence this leads to higher rates of surgical failure in these cases
The third reason for failure is that acral areas are more difficult to operate. The reason of difficulty being two fold i.e. difficult to dermabrade the acral areas and difficulty in immobilizing the grafted area i.e. in retaining the transplanted tissue grafts (Punches, Ultrathin skin grafts ), cellulargrafts (cultured and non cultured autologous cell suspensions). Hence if adequate depths are not achieved while deepitheliazing the recipient area and area is not adequately immobilized the cell/ graft uptakes will be poor and hence result in partial or poor depigmentation
When we use the term acral vitiligo we broadly include these sites Fingers, toes, Lips, nipples, peri areola, genitalia, peri-anal Dorsum of the hand and feet Lateral and medial malloelus, knees, elbows
These areas are often clubbed as the Lip tip type of vitiligo or the bony vitiligo or acral vitiligo. Besides being notorious to treat all these areas have these characteristics in common
There are almost no or few hair follicles on these sites
They are difficult to dermabrade e.g. the penis, lips, and vaginal patches
It’sdifficult to immobilize and retain the grafts on these sites e.g. the penis, lips, vaginal patches
These patches show some disease activity
Hence they are all labeled as difficult to treat area
The irony in acral vitiligo is that the difficult areas are also the most visible areas and thus they become the most important areas to be treated
Vitiligo after all is a benign cosmetic disease with malignant psychological issues and it’s the acral areas that are the ones which produce most stress and psychological issues in vitiligo patients
Coming to management of acral vitiligo as has been discussed endless medical treatments are not only futile but dangerous if we actually consider the long durations for which some patients of acral vitiligoare subjected to systemic steroids, immunosuppressive, UV radiations when it is quite evident that these areas are unlikely to repigment unless the melanocytes are replaced.
It is important for the treating dermatologist to understand and acknowledge the fact that beyond a certain limit medical treatment will not work and its best to replace the missing cell i.e.the melanocytes with a surgical procedure which he or she is apt at.
The surgical management of acral vitiligo can be classified as
- Procedures in which melanocytes are being replaced i.e. the tissue grafts and the cellular grafts
Tissue grafting: Mini punch grafting, ultra thin split thickness grafting, blister grafting10, hair follicle grafts, smash grafts
Cellular Grafting: Cultured11 and non cultured autologous cell suspensions
- Procedures in which melanocytes are not being replaced i.e.tattooing, excision and closure, dermabrasion or chemabrasion
How to choose a surgical modality i.e. which type of procedure is best suited for which area
Vitiligo is a cosmetic disease and this should never be forgotten when surgical procedure is being planned. The end result should be a match as close to the surrounding skin in terms of texture and color matching, there should be no alteration in the functionality or the shape or size of the recipient area
Also in the process of depigmenting the recipient large areas of donor areas should not be disfigured or scarred permanently
If the surgical end point can’t fulfill the above criteria it defeats the whole purpose of surgery
All the above mentioned procedures can produce varying amount of depigmentation but have their own advantages and disadvantages
Tattooing or micro pigmentation is a process in which artificial pigments are introduced into the mid dermis level of the vitiligo lesion. In most cases the final color matching is very poor and barring few areas like the angles of the mouth, this procedure should be avoided in all patients.
The tattooed particle imparts a bluish tinge in the vitiligo skin and it is difficult to correct with other surgical procedures.
Excision and closure of the vitiligo patch is also a procedure with limited use since it can be carried out only in cases of small patches and it will always end up with a linear suture scar line
Dermabrasion or chemabrasion is a treatment modality which works primarily in the hairy areas as the process of therapeutic wounding stimulates the inactive melanocytes present in the outer root sheath of the hairs. Since most acral areas are non hair bearing area just dermabrasion not followed by grafting procedures will fail to produce results
Mini punch grafting is the simplest vitiligo surgery but invariably produces cobble stone appearance at the recipient and donor site and the target like appearance of the repigmentation is not well accepted by the patients
Suction blister grafting produces good cosmetic results esp. on the lips however it is a time consuming procedure and only small areas can be taken up at one time because of small sized grafts
Ultra thin split thickness grafting can be used for large areas however it is a highly skilled based procedure not all surgeons can harvest ultrathin grafts and the grafts may give a stuck on appearance, hyper pigmentation and hypertrophy, perigraft halo and milia formation are other issues commonly encountered. Also the biggest disadvantage is that large sheets of donor area skin are required which in many cases may produce scarring at the donor site.
Cultured melanocyte grafting is an excellent procedure where melanocytes can be expanded by 100 times with a very small donor area; this process is limited because of the requirement of an elaborate tissue culture lab which makes the process very expensive
Non cultured epidermal cell suspension can be used to treat large areas with small donor area (5- 10 times expansion) the color and texture matching is excellent
with no stuck on appearance, no cobble stoning, it does require training but elaborate culture labs and equipment are not required
Even though most dermatoid surgeons will have their favorite techniques the noncultured autologous epidermal cell suspension scores over most techniques
It’s a cellular graft so no texture, shape functionality alterations will occur at the recipient site, no cobblestone look, no milia formation, no stuck on graft look
Since the cells can be expanded 5-10 times a very small donor area is required so no or minimum scarring at the donor site
Immobilization of the recipient area in the acral is easier as there is no tissue graft to hold
Preoperative counselling and Informed consent.13
The entire process starts with detailed history of the patient pertaining not only to vitiligo but general health and associated diseases. The patient needs to be properly counselled about the procedure and the pre and post op care
A detailed consent form elaborating the procedure and possible complications should be signed by the patient. The patient is informed of the nature of the disease. The consent form should specifically state the limitations of the procedure, and the possibility that the NCECS is replacement of functional melanocytes into the vitiligo area which is devoid of melanocytes and the disease can become unstable again in the future and there can be a loss of pigment on other sites as well as operated sites and if the disease shows future progression additional medical line of treatment and or procedures will be needed for proper results. The patient is also counselled that he/she may require additional medical treatments and or phototherapy post op to stimulate pigmentation on the operated patches and that it can take a few months to a year for significant repigmentation and colour match
Preoperative laboratory studies include complete haemogram including platelet counts, bleeding and clotting time (or prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time), Thyroid profile, LFT, KFT, serum electrolytes, Chest X ray PA view, ECG in adults. Screening for antibodies for hepatitis B, C and HIV is recommended.
Anesthesia
Small areas can be managed under topical and or local anesthesia in an OT as a day care procedure.
If a case is being done under local lignocaine (2%) with or without adrenaline is generally used. Maximum dosage that can be used is 4.5mg/kg (up to 300 mg) and with epinephrine 7 mg/kg (up to 500mg) Larger areas may need regional blocks or IV sedation
Procedure of preparing the autologous melanocyte cell suspension
The steps involved in this process are
- Harvesting a Skin graft from the Thigh
- Trypsinization and Cell separation
- Dermabrasion of the recipient (vitiligo) site
- Transfer and fixing of melanocyte rich cell suspension
Harvesting of Skin Graft
The lateral aspect of the gluteal region is selected as the donor area. Care should be taken to ensure that the Donor area had no vitiligo patches. The size of the split-thickness donor skin takenis one-tenth of The recipient area while dealing with large confluent patches. In cases having multiple scattered small patches, larger donor skin is taken – approximately one-fifth of the recipient area. Under aseptic precautions, a very superficial sample is harvested using a shaving blade held in straight Kocher’s forceps. The donor area is dressed with liquid paraffin dressing tulle (Fairlee™) and sterile gauze pad.
Trypsinization and Cell separation technique
The cell separation was done under aseptic precautions in a laminar flow bench kept in the operation theatre. The skin sample harvested is transferred to a Petri dish containing 5 ml of the 0.2% w/v trypsin solution, epidermal side facing upwards, and incubated for 45 min at 37°C. After 45 min, the action of trypsin is neutralized with trypsin inhibitor (Life Technologies, USA).The epidermis is separated from the dermis and transferred (epidermis) to a test tube containing 2 ml of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium: Nutrient Mixture F-12 (DMEMF/12) medium (Life Technologies) and vortex mixed for 15 s.
The epidermis is further broken into smaller pieces in a Petri dish and washed with the DMEM F/12 medium and finally transferred to a test tube containing the DMEM F/12 medium and centrifuged for 6 min. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was suspended in a 1-ml insulin syringe The final volume prepared varied from 0.2 to 0.5 ml depending on the size of the area to be treated.
Derambrasion of the recipient site
The recipient site is abraded with a dermabrader fitted with a diamond fraise wheel (Delasco™) While operating close to the eyelid margins, an Erbium: YAG laser is usedwith a fluence of 1000 mJ, 1–2 passes. The endpoint of ablation is pinpoint bleeding. Haemostasis is achieved and the ablated area is covered with saline-soaked gauze pieces.
Transplantation technique
The cell suspension is spread evenly on the dermabraded area and covered with collagen dressing (Collomedica Laboratories) to hold the cells applied This is covered with liquid paraffin and gauze pieces. Patients are instructed to lie still in the same position for at least 1 h to ensure cell fixation and then shifted to a room and further instructed to avoid excessive movements of the treated area for at least 6 h.
Post-procedure instructions
All patients are instructed to take complete rest and avoid all vigorous physical activities. Patients are Prescribed oral antibacterial agents for 5 days and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for 3 days. The dressings are removed after 1 week in most cases. Patients are asked to follow up at weeks 1 and 3, and then at 3-month intervals. Patients were instructed not to scrub the area and postprocedureno medication was prescribed. Patients were permitted to use make-up on the treated area 10 daysafter the removal of dressings.
Certain Modifications of the procedure for specific acral area
Since acral areas are difficult to operate because of the difficulty of dermabrasion and retaining the cells transferred these techniques can be used to improve the results over specific acral sites
How I do it!!! Eyes
- Dermabrasion
- Use cylindrical burs
- Stabilize well
- Use a corneal shield to provide base for DA
- Immobilization
- Small areas only collagen leave it open
- Larger area ( full eyelid) collagen>> paraffin>> guaze>> pad>> close eye for 7 daysHow I do it Finger tips!!!
- Dermabrader
- Deeper DA
- Immobilization
- Dress each finger individually and then the whole hand
How I do it Lips!!!
- Dermabrasion
- Use bigger wheels
- Put a guaze inside mouth to make the lips taut
- Use the co2 laser or erbium YAG Laser
- Immobilization
- Collagen>> Paraffin>> tie up with 4-0 prolene
Specific issues with surgery over penis / scrotum
- The length & girth will keep varying
- Temperature, anxiety, sleep, all can alter the tumescence of penis
- Scrotum skin can considerably contract & expand
How I do it Penis / scrotum
- Dermabrasion
- Pear shaped bur
- Pinch skin around to make it taught
- Immobilization
- Collagen pixel
- Put in a catheter
- Admit patient
- Drugs to reduce erection Discussion
The advent of vitilgo surgery has definitely changed the treatment outcomes of vitiligo esp. in the acral and segmental variety; and in vitiligo surgery it is the autologous non cultured cell suspension technique which has totally revolutionized the surgical options and has taken the patient and doctor satisfaction to the highest level.However it’s important that before we subject any patient to any vitiligo surgery we have a detailed discussion regarding the advantages, disadvantages, limitations of the treatmentEach patient should be counseled about the risk of failure, riskof incomplete repigmentaion, colour, texture mismatch, and most of all the risk of recurrence. Vitiligo is an autoimmune disease and it can have its phases of stability and activity, surgical procedures should be taken up only in cases which are at least one year stable and in most patients medical treatment may be need to continued even post surgery to keep the autoimmune process in check.Every patient of vitiligo is an individual and the treatment surgical or medical should be customized or tailor made according to the type, extent, stability of the disease, equal consideration need to be given to the medical condition of the person i.e. age, family history, co morbidities e.g. diabetes, hypertension etc. we should keep a watch out for the potential side effects of the medical treatment i.e. medications, lasers, lights.Hence a holistic approach keeping all these Factors in mind will provide a ray of hope to the cases of vitiligo.
Book An Appointment